Visual Comparison
Absorption and adsorption are two fundamental processes in chemistry and material science that describe how substances interact with materials. While absorption involves the penetration of one substance into the bulk of another, adsorption refers to the adhesion of molecules onto a surface. Understanding these differences is crucial for applications in chemistry, environmental science, and industrial processes.
What is Absorption?
Absorption is the process in which a substance, such as a gas or liquid, is fully taken up into the volume of another substance. For example, a sponge soaking up water demonstrates absorption. The absorbed substance diffuses throughout the material, making it a bulk phenomenon.
What is Adsorption?
Adsorption is the process in which molecules adhere only to the surface of a material without penetrating its bulk. Activated carbon filtering toxins from water is a common example of adsorption. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon and is widely used in catalysis, purification, and chemical sensors.
Absorption vs Adsorption: Detailed Comparison
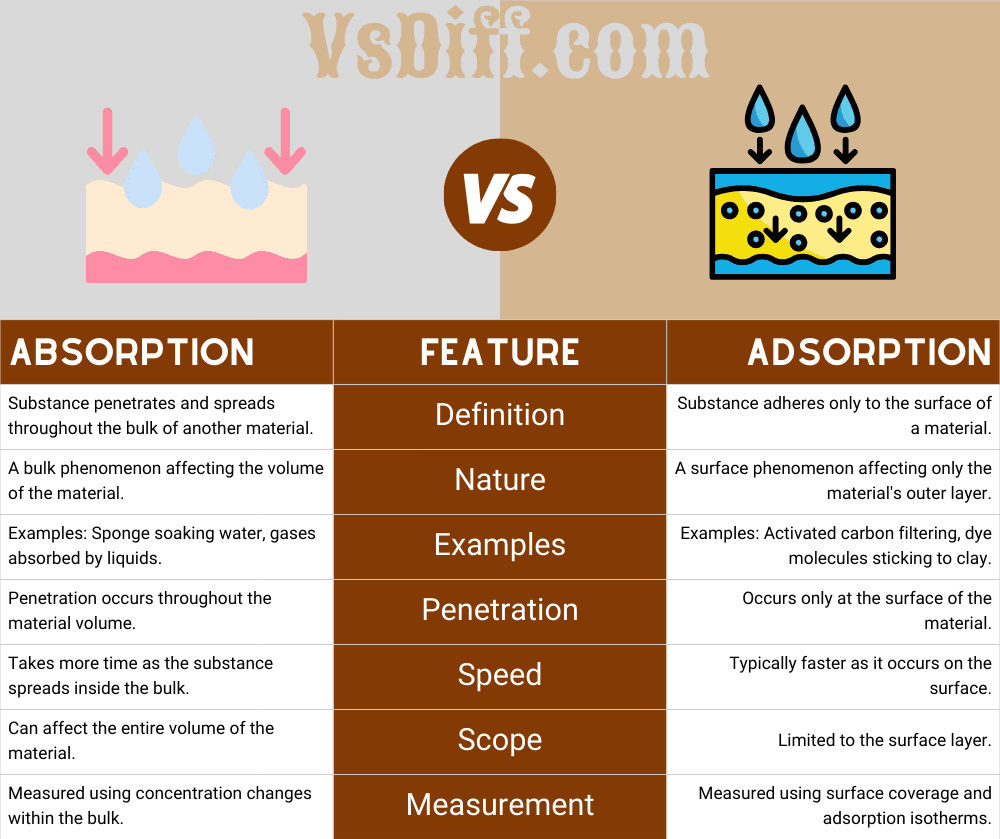
| Absorption | Feature | Adsorption |
|---|---|---|
| Substance penetrates and spreads throughout the bulk of another material. | Definition | Substance adheres only to the surface of a material. |
| A bulk phenomenon affecting the volume of the material. | Nature | A surface phenomenon affecting only the material’s outer layer. |
| Examples: Sponge soaking water, gases absorbed by liquids. | Examples | Examples: Activated carbon filtering, dye molecules sticking to clay. |
| Penetration occurs throughout the material volume. | Penetration | Occurs only at the surface of the material. |
| Takes more time as the substance spreads inside the bulk. | Speed | Typically faster as it occurs on the surface. |
| Can affect the entire volume of the material. | Scope | Limited to the surface layer. |
| Measured using concentration changes within the bulk. | Measurement | Measured using surface coverage and adsorption isotherms. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can absorption and adsorption occur simultaneously?
Yes, in some cases, a substance can both penetrate the bulk and adhere to the surface of a material. However, the dominant process depends on the material properties and conditions.
2. Which is faster: absorption or adsorption?
Generally, adsorption is faster because it occurs only on the surface, while absorption requires the substance to diffuse through the entire volume of the material.
3. Can adsorption affect the entire material?
No, adsorption is limited to the surface layer, whereas absorption can affect the entire volume of the material.
4. What are common applications of absorption and adsorption?
Absorption is used in sponges, liquid-gas absorption in chemical processes, and moisture uptake. Adsorption is widely used in water purification, air filtration, catalysis, and sensors.
5. How are absorption and adsorption measured?
Absorption is usually measured by changes in concentration within the bulk material, while adsorption is measured by surface coverage or adsorption isotherms.