Visual Comparison
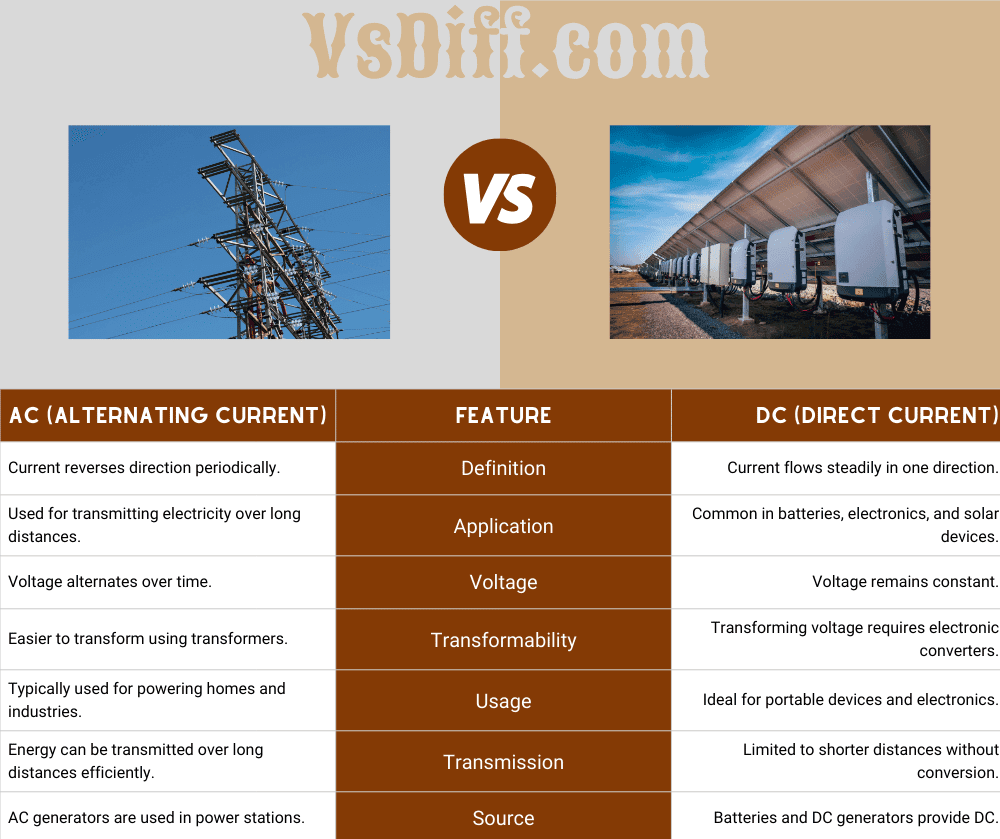
Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) are the two main types of electric current used in power systems worldwide.
AC periodically reverses direction, while DC flows consistently in one direction.
Grasping their differences is essential for electrical engineering, electronics, and daily applications like household power and batteries.
What is Alternating Current (AC)?
AC is an electric current that changes direction periodically.
It is widely used for transmitting electricity over long distances because it is easy to step up or down using transformers.
Household power outlets supply AC, which allows efficient distribution of energy.
What is Direct Current (DC)?
DC is an electric current that flows steadily in one direction.
It is commonly found in batteries, solar cells, and electronic devices.
DC is ideal for applications requiring stable voltage and consistent power supply.
AC vs DC: Detailed Comparison
| AC (Alternating Current) | Feature | DC (Direct Current) |
|---|---|---|
| Current reverses direction periodically. | Definition | Current flows steadily in one direction. |
| Used for transmitting electricity over long distances. | Application | Common in batteries, electronics, and solar devices. |
| Voltage alternates over time. | Voltage | Voltage remains constant. |
| Easier to transform using transformers. | Transformability | Transforming voltage requires electronic converters. |
| Typically used for powering homes and industries. | Usage | Ideal for portable devices and electronics. |
| Energy can be transmitted over long distances efficiently. | Transmission | Limited to shorter distances without conversion. |
| AC generators are used in power stations. | Source | Batteries and DC generators provide DC. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can AC be converted to DC?
Yes, AC can be converted to DC using rectifiers. This is common in electronics that require steady voltage.
2. Why is AC used for home power supply?
AC is easier to transmit over long distances and can be stepped up or down using transformers, making it efficient for households and industries.
3. Is DC safer than AC?
Safety depends on voltage and current. Low-voltage DC is often safe, but high-voltage DC or AC can both be dangerous.
4. Which is more efficient for electronic devices?
DC is more efficient for devices like computers and smartphones since it provides stable voltage.
5. Can AC and DC be used together?
Yes, many systems convert AC to DC or DC to AC to suit different applications, such as in solar power systems or power adapters.