Understanding JPEG vs PNG
JPEG and PNG are two of the most common image formats used across the internet. While both deliver digital images, they serve different purposes based on compression, quality, and transparency support. Knowing when to use JPEG or PNG can improve website performance, design quality, and storage efficiency.
What is JPEG?
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a lossy compression format widely used for photographs and web images. It reduces file size by discarding some data, making it ideal for fast-loading websites and online sharing. However, JPEG images lose detail if repeatedly edited and saved.
What is PNG?
PNG (Portable Network Graphics) is a lossless compression format that preserves all image details without quality loss. It supports transparency and sharp edges, making it perfect for logos, icons, and images requiring high clarity. The trade-off is larger file sizes compared to JPEG.
Why Do JPEG and PNG Differ?
The core difference lies in compression. JPEG sacrifices some detail for smaller files, while PNG retains every pixel but requires more storage space. This fundamental trade-off determines which format is better for photos, graphics, or professional designs.
When Should You Use Each Format?
- Use JPEG for: photographs, social media images, product photos, and situations where file size matters more than maximum quality.
- Use PNG for: logos, digital art, screenshots, text-heavy images, and cases requiring transparency.
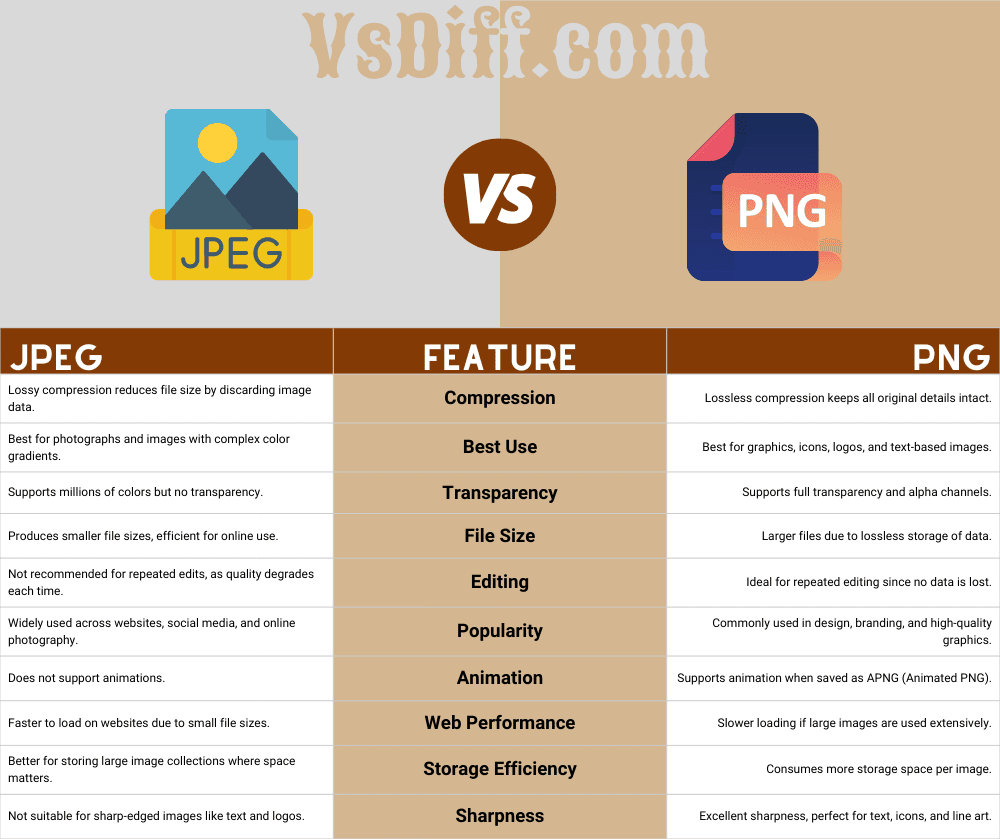
JPEG vs PNG: Side-by-Side Comparison
| JPEG | Feature | PNG |
|---|---|---|
| Lossy compression reduces file size by discarding image data. | Compression | Lossless compression keeps all original details intact. |
| Best for photographs and images with complex color gradients. | Best Use | Best for graphics, icons, logos, and text-based images. |
| Supports millions of colors but no transparency. | Transparency | Supports full transparency and alpha channels. |
| Produces smaller file sizes, efficient for online use. | File Size | Larger files due to lossless storage of data. |
| Not recommended for repeated edits, as quality degrades each time. | Editing | Ideal for repeated editing since no data is lost. |
| Widely used across websites, social media, and online photography. | Popularity | Commonly used in design, branding, and high-quality graphics. |
| Does not support animations. | Animation | Supports animation when saved as APNG (Animated PNG). |
| Faster to load on websites due to small file sizes. | Web Performance | Slower loading if large images are used extensively. |
| Better for storing large image collections where space matters. | Storage Efficiency | Consumes more storage space per image. |
| Not suitable for sharp-edged images like text and logos. | Sharpness | Excellent sharpness, perfect for text, icons, and line art. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Which is better quality: JPEG or PNG?
PNG generally offers better quality because it uses lossless compression, while JPEG sacrifices detail to reduce file size.
2. Do PNG images always look sharper?
PNG images can look sharper, especially for text and logos, but JPEG is often sufficient for photographs with natural gradients.
3. Why are PNG files larger than JPEG files?
Because PNG does not discard any image data, its file size is larger compared to JPEG’s lossy compression.
4. Can JPEG support transparency like PNG?
No, JPEG does not support transparency. PNG is the preferred choice for transparent images.
5. Which format is best for web use?
For photos, JPEG is best due to small size and fast loading. For graphics or images requiring transparency, PNG is the superior choice.